What are Endodontic Dental Services?
Endodontic dental treatment essentially refers to root canals. When a tooth has had irreversible damage to the nerve, there are only two options: either the tooth has to be extracted, or an attempt can be made to save the tooth via a root canal. Root canals (endodontics) involve several considerations, and sometimes a tooth is better off being extracted than being saved. For every root canal contemplated, and before we can begin endodontic treatment, we must look at how much original tooth remains as well as its periodontal (gum) condition and the relevant biting forces on the tooth.
In a root canal, our goal is to clean out all the dead and dying material from inside the tooth and refill the canals to prevent reinfection by bacteria. This is where using a microscope really helps the result, as some of those canals are so hidden that trying to find them without a microscope would be like finding your keys in the dark. The attached photos of a root canal case are x-rays, because externally, a tooth looks basically the same before and after a root canal. You will see on the image that the inside of the tooth is filled up from top to bottom.
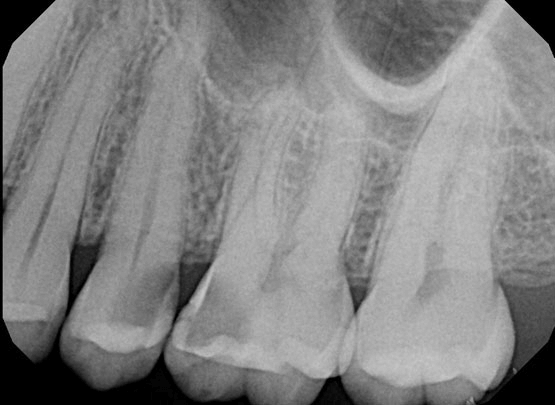
Root Canal – Before
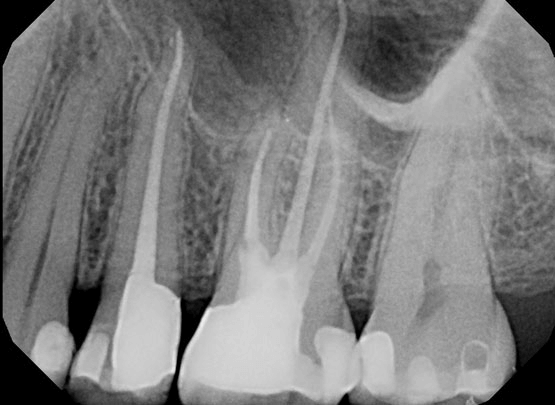
Root Canal – After
Root canals on teeth 25 and 26 (upper left second premolar and first molar), done because of obvious pulpal decay (decay into the nerve) on both teeth. In these cases, there are only two appropriate options: extraction of teeth, or root canals to preserve them. This patient opted to save both teeth by having root canals done on both teeth. Later, he would go on to have crowns on both teeth to prevent fractures of the teeth.
Teeth: 25 and 26
25 – 1 canal, symptomatic irreversible pulpitis, normal apical tissues
26 – 4 canals, symptomatic irreversible pulpitis, normal apical tissues
Condition of teeth on access: hyperemic
Final canal instrumentation:
25: WL = 24mm instrumented to 35/0.04
26: MB1: 19mm to 35/0.04 MB2: 19mm to 35/0.04 DB: 19mm to 35/0.04 P: 22mm to #40 SS file
Both teeth irrigated with NaOCl(aq) and 17% EDTA (aq) with Piezoelectric ultrasonic activation, obturated with gutta percha and Kerr RCS via System B downpack and Obtura backfill. Final fillings were completed with Air abrasion/phosphoric acid etch/Kerr Optibond FL/Ultradent Permaflo Purple on orifices/Dentsply Esthet-X flowable A1/Esthet-X A3. Treatment complete under Global Surgical Operating Microscope.

